In cybersecurity, vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-21298 highlight the critical need for proactive risk identification and mitigation. This flaw in Windows Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) allows attackers to execute remote code, posing significant risks to organizations. While CVE-2025-21298 primarily impacts internal systems, understanding its implications helps underline the importance of external attack surface management tools like TRaViS ASM.
What is CVE-2025-21298?
CVE-2025-21298 is a critical vulnerability that exploits a "Use After Free" weakness in Windows OLE. The vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.8 (CRITICAL), meaning it can:
- Be exploited remotely with no user interaction.
- Affect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of systems.
- Lead to complete system compromise.
Affected systems span legacy platforms such as Windows Server 2008 to modern releases like Windows 11 and Server 2025, making patching and internal security essential.
What Is a CVE?
CVE stands for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures, which is like a standardized ID system for known security flaws in software. Think of it as a catalog entry that helps cybersecurity experts talk about and fix specific problems.
This particular vulnerability exists in a part of Windows called Object Linking and Embedding (OLE). OLE is a technology that allows different programs to work together. For example, it lets you embed an Excel spreadsheet inside a Word document.
The problem is caused by something called a "Use After Free" bug. This is a type of programming error where a program tries to use a piece of memory (basically a temporary workspace in the computer) after it has already been discarded. When this happens, hackers can sneak into the computer and trick it into doing something harmful.
Why CVE-2025-21298 is Alarming
The key reasons this vulnerability is critical include:
Ease of exploitation: It has low attack complexity, making it an attractive target for attackers.

Impact: Exploits can result in severe data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage.

Widespread use of affected systems: Many organizations still rely on vulnerable or un-patched systems.
Can TRaViS ASM Address CVE-2025-21298?
TRaViS ASM is purpose-built for external attack surface management, focusing on vulnerabilities in internet-facing assets. While CVE-2025-21298 is primarily an internal system vulnerability, TRaViS can indirectly support mitigation by:
Detecting External Attack Vectors

If an organization exposes systems vulnerable to CVE-2025-21298 through public interfaces, APIs, or misconfigurations, TRaViS can detect these openings and alert your team.
Continuous External Monitoring
Preview of the elements it examines:
- Exposed credentials
- Open ports
- Publicly accessible endpoints
- Misconfigurations that could lead to exploitation by attackers
- Dark Web Intel
- CVE's
- IP's
This external visibility ensures no internal vulnerabilities are unintentionally exposed.
Integration with Threat Intelligence
TRaViS integrates with threat intelligence sources to provide context about vulnerabilities, including related exploit activity on the dark web.
While it doesn’t directly detect CVE-2025-21298 within internal systems, it highlights external risks that could act as a gateway for exploitation.
Broader Implications of External Vulnerabilities
While CVE-2025-21298 demonstrates the dangers of internal system weaknesses, many breaches begin with externally exposed assets. Tools like TRaViS ASM help by:
- Reducing the external attack surface through proactive monitoring.
- Identifying high-risk misconfigurations that connect internal systems to external threats.
- Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on exploit-ability and risk level.
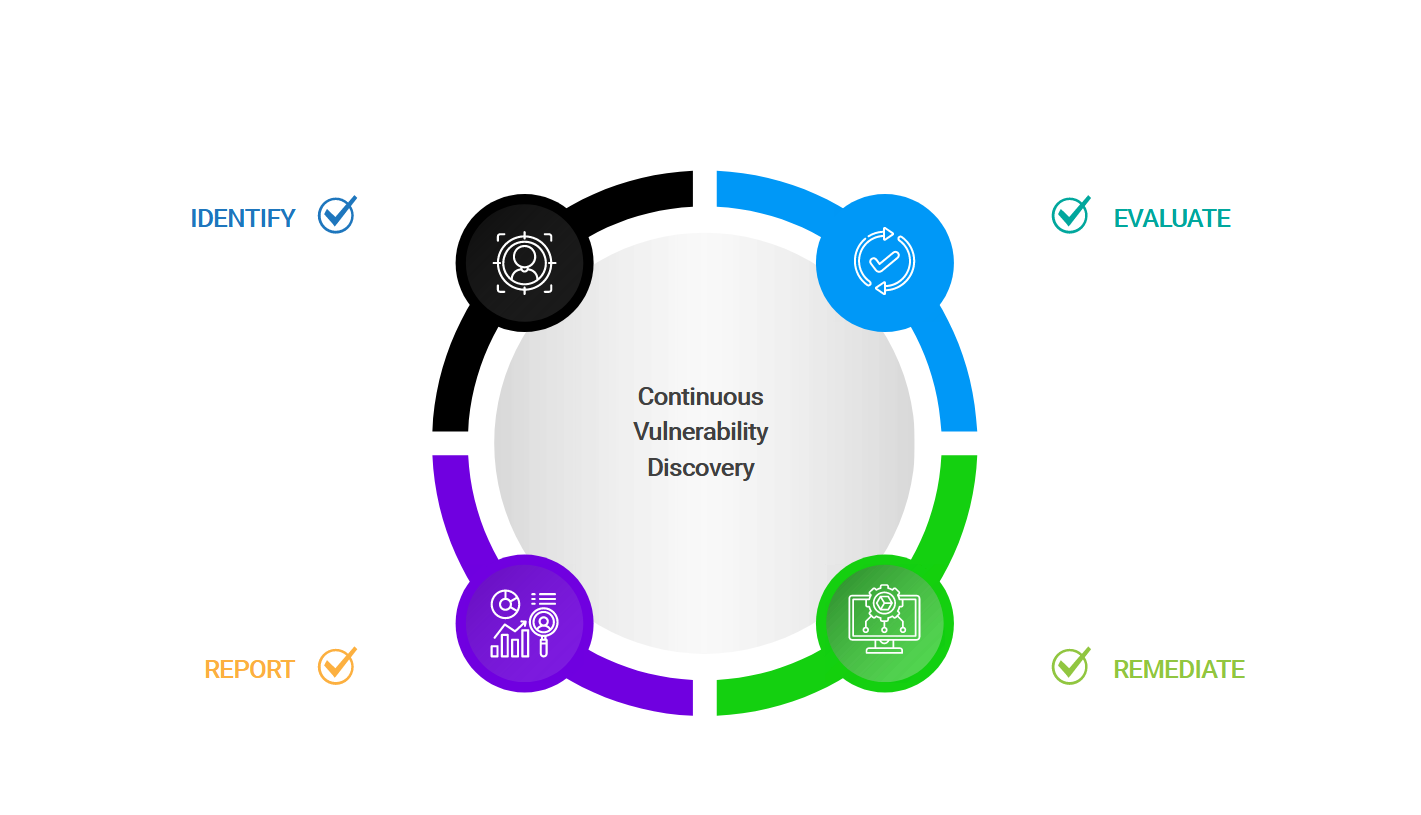
What Can Organizations Do Today?
Patch Internal Systems
Apply Microsoft’s patches for CVE-2025-21298 across all affected systems. Addressing these vulnerabilities promptly is essential to prevent potential remote code execution.
Strengthen External Security
Review your external assets to ensure they don’t expose internal systems to risk. Key actions include:
- Identifying and securing exposed endpoints.
- Limiting unnecessary public access.
- Regularly scanning for misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
Educate Your Teams
Cybersecurity awareness and training are vital. Equip your team with the knowledge and tools to recognize and address potential threats proactively.
Securing Your External Attack Surface
CVE-2025-21298 underscores the importance of robust security measures both internally and externally. Continuously monitor and manage your publicly exposed assets to reduce risks and enhance your cybersecurity posture. Consider adopting tools or strategies that offer proactive protection against emerging threats.





